ColorFinder¶
Methods to find and interact with complex color objects on the MainScreen.
TColorFinder Zoom
When designing a TColorFinder it’s very important to keep in mind that all values that are not colors are measured in pixels at 50% zoom.
It is okay to be slightly off, but the closer you are to 50% the better.
This is important because when you use TColorFinder.Find methods, the values of the
TColorFinderwill be transformed into your current zoom and assumes 50% as the baseline.For example, say you want to
growthe object by 54 pixels at 50%. At 0% zoom, 54 pixels is much much larger than 54 pixels at 50% zoom. Because of this we transform it, assuming that you gathered your measurements at 50% zoom and transform it to 0% zoom which in this example would be 19 pixels.So if you grow your object by 54 pixels at 50% zoom you will only grow it by 19 at 0% zoom. At 100% zoom you grow it by 148 pixels. And so on.

A finder working at different zoom levels producing similar results.¶
TColorFinder Colors and ColorClusters
TColorFindersare extremely good at finding complex color objects because you can add multiple colors or color clusters and values to process what is found in a way that filters what you don’t want out while keeping what you want.You can add as many colors and color clusters you want, but you should use a sensible amount as the more you add the slower your finder will be. If you need more than 5/6 colors and/or clusters together you might not be doing things right or you need a different approach.
TODO: ADD COLOR AND COLORCLUSTERS USAGE EXAMPLE with the following figure or something similar:
TRSObjectFinder.Colors
An color array which will searched for. Use ACA to acquire color(s).
Finder.Colors += CTS2(2503237, 20, 0.10, 0.14); // brown Finder.Colors += CTS2(5526875, 15, 0.19, 0.06); // grey

The two colors above found and merged together.¶
TRSObjectFinder.ColorClusters
An array of “color clusters” which will be merged together. Use ACA to acquire color(s).
A “color cluster” consists of a
primaryandsecondarycolor and adistancevalue. When searched for onlyprimarycolors withindistanceofsecondarycolors are returned.
Finder.ColorClusters += [
CTS2(2503237, 20, 0.10, 0.14), // brown
CTS2(5526875, 15, 0.19, 0.06), // grey
2 // distance
];

The above color cluster found where “brown” is within 2 pixels of “grey”.¶
TColorFinderTransformer¶
Helper record that helps transforming a TColorFinder after finding it’s colors and/or colors clusters.
You can access the TColorFinder transformer through the
TColorFinder.Transformer variable.
TColorFinderTransformer.Grow The amount to
Growwhat we found. This is useful for filling gaps.Finder.Transformer.Grow := 2;
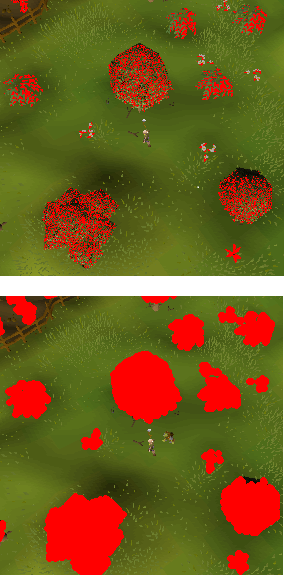
Grow before and after.¶
TColorFinderTransformer.Erode The amount to
Erodewhat we found. This is useful for removing small amounts of noise.Finder.Transformer.Erode := 2;

Erode before and after.¶
Erodecomes afterGrowand they can be paired together for some powerful results.Finder.Transformer.Grow := 3; Finder.Transformer.Erode := 4;

Grow paired with Erode.¶
TColorFinderTransformer.Distance This is the distance that decides how multiple objects are grouped up.
Distance=5would mean that points that are closer than or equal to 5 pixels away are considered close enough to merge into a singular group.Finder.Transformer.Distance := 5;

Cluster distance 5 produces four individual chairs¶
Finder.Transformer.Distance := 20;

Cluster distance 20 produces two sets of chairs¶
TColorFinderTransformer.ShortSide and TColorFinderTransformer.LongSide Used to filter the final results.
For each of the results, the bounding
TQuadis used,TQuadshave a long and a short side which is measured in pixels. Any match whoseTQuadis not within theShortSize.Min/ShortSide.MaxandLongSide.Min/LongSide.Maxwill be removed from the final result.// Removes matches where the short side isn't within 10 and 20 pixels Finder.MinShortSide := 10; Finder.MaxShortSide := 20; // Removes matches where the long side isn't within 20 and 40 pixels Finder.MinLongSide := 20; Finder.MaxLongSide := 40;

Example bounding rectangle with a long and short side.¶
TColorFinderTransformer.Normalize¶
function TColorFinderTransformer.Normalize(): TColorFinder;
Helper method to normalize a TColorFinderTransformer from 50% zoom values to our current one with the help of MainScreen.NormalizeDistance. This is important to do so we have consistent values at any zoom value.
TColorFinderTransformer.Process¶
function TColorFinderTransformer.Process(tpa: TPointArray): T2DPointArray;
Helper method to transform a TPA with the current TColorFinderTransformer into an ATPA.
TColorFinder¶
Main record used to find and interact with complex color objects.
TColorFinder.Find¶
function TColorFinder.Find(out atpa: T2DPointArray; areas: TBoxArray): Boolean;
function TColorFinder.Find(out atpa: T2DPointArray; areas: TPolygonArray): Boolean; overload;
function TColorFinder.Find(out atpa: T2DPointArray; areas: TCuboidArray): Boolean; overload;
function TColorFinder.Find(out atpa: T2DPointArray): Boolean; overload;
Attempts to find on the given area a TColorFinder.
If area is not specified, MainScreen Bounds are used.
The function returns true if we find anything and the coordinates containing
what was found are returned through atpa.