Login¶
The login screen is the first screen you see when you open a client and it finishes loading:
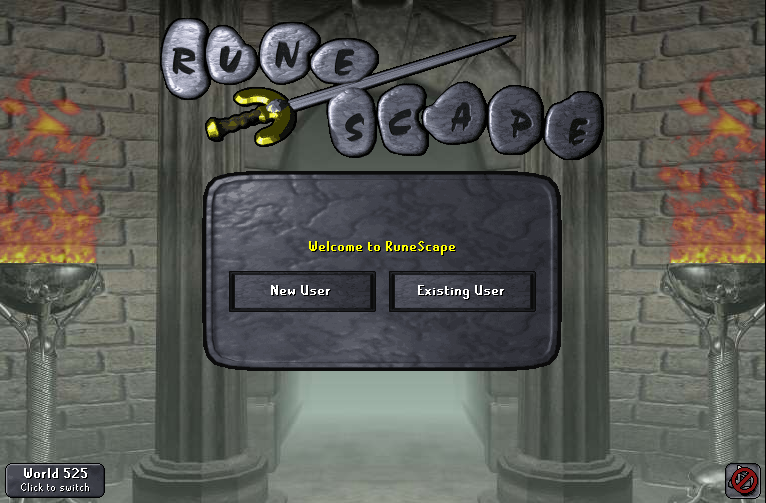
WaspLib’s TRSLogin can handle both resizable and fixed mode login screens.
Login Messages¶
const
LOGIN_MESSAGES = [
'Welcome to RuneScape',
'Connecting to server',
...,
'Authenticator'
];
Constant of all the login messages the login screen can handle.
Login Enums¶
ERSLoginMode = enum(UNKNOWN, LEGACY, LAUNCHER);
ERSLoginButton = enum(LAUNCHER, EXISTING_USER, LOGIN, RETRY, OKAY, CONTINUE);
ERSLoginInput = enum(USERNAME, PASSWORD);
ERSLoginMessage = enum(UNKNOWN, WELCOME, ..., AUTHENTICATOR);
Enums representing various aspects of the login screen.
ERSLoginMessage is a enum representation of Login Messages.
TRSLogin¶
Main record responsible for handling the Login screen.
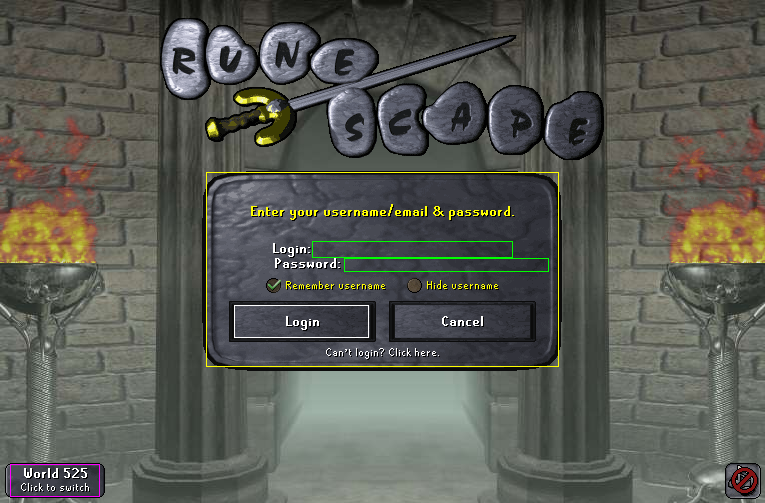
The login screen.¶
Login.Setup¶
procedure TRSLogin.Setup();
Internal method responsible for setting up the TRSLogin coordinates. This is automatically called for you on the Login variable.
Login.SelectInput¶
function TRSLogin.SelectInput(field: ERSLoginInput): Boolean;
Attempts to select the specified ERSLoginInput, returns True if we succeed.
This waits a few milliseconds for the flashing yellow cursor for confirmation.
Example:
WriteLn Login.SelectInput(ERSLoginInput.USERNAME);
Login.InputIsFilled¶
function TRSLogin.InputIsFilled(field: ERSLoginInput): Boolean;
Returns True/False if the specified field is filled.
Example:
WriteLn Login.InputIsFilled(ERSLoginInput.USERNAME);
Login.ClearInput¶
function TRSLogin.ClearInput(field: ERSLoginInput): Boolean;
Attempts to clear the specified field.
Example:
WriteLn Login.ClearInput(ERSLoginInput.USERNAME);
Login.FillInput¶
function TRSLogin.FillInput(field: ERSLoginInput; details: String): Boolean;
Attempts to fill the specified field with details.
Example:
WriteLn Login.FillInput(ERSLoginInput.USERNAME, 'myprofile@email.com');
Login.GetMessage¶
function TRSLogin.GetMessage(): ERSLoginMessage;
Returns the currently visible login message as a ERSLoginMessage.
Check Login Enums for more information on ERSLoginMessage.
Example:
WriteLn Login.GetMessage();
Login.GetMode¶
function TRSLogin.GetMode(): ERSLoginMode;
Returns the current login mode as a ERSLoginMode.
The login mode can only be known from the “Welcome to RuneScape” screen.
Check Login Enums for more information on ERSLoginMode.
Example:
WriteLn Login.GetMode();
Login.HandleWelcome¶
function TRSLogin.HandleWelcome(): Boolean;
Attempts to handle the “Welcome to RuneScape” screen regardless of the
ERSLoginMode the client is on.
Check Login Enums for more information on ERSLoginMode.
Example:
WriteLn Login.HandleWelcome();
Login.Back2Welcome¶
function TRSLogin.Back2Welcome(): Boolean;
Attempts to return to the “Welcome to RuneScape” screen. This is used to handle any screen that has an “Ok” button. Returns True if we succeed.
Example:
WriteLn Login.Back2Welcome();
Login.EnterCredentials¶
function TRSLogin.EnterCredentials(username, password: String): Boolean;
Attempts to enter a user credentials.
Example:
WriteLn Login.EnterCredentials('username', 'password');
Login.Retry¶
function TRSLogin.Retry(msg: ERSLoginMessage): Boolean;
Attempts to handle any screen that has a “Retry” button. Returns True if we succeed.
The current ERSLoginMessage message has to be passed as msg so we know
when we successfully handled the button.
Login.HandleError¶
function TRSLogin.HandleError(msg: ERSLoginMessage): Boolean;
Attempts to handle any screen that has an error message. Returns True if we succeed.
The current ERSLoginMessage message has to be passed as msg so we know
when we successfully handled the current error.
Everytime this function is called, the internal Login.Attempts variable is
increased.
After 10 times of this being called without Login.Attempts being reset, this
will raise an exception IF the reason we can’t login is not the world being
full. IF the reason is the world being full, this can be called forever.
Login.HandleMessage¶
function TRSLogin.HandleMessage(msg: ERSLoginMessage; username, password: String): Boolean;
Attempts to handle whatever screen the login screen is currently at. Returns True if we succeed.
The current ERSLoginMessage message has to be passed as msg so we know
when we successfully handled the current error.
The profile username and password we want to use also have to be passed in.
This can be empty value if we are using the Jagex Launcher, e.g.: '', ''.
On certain ERSLoginMessages that cannot be handled this will raise an
exception to shutdown your script. For example, if the profile you are trying to
use has been banned.
Login.DoLogin¶
function TRSLogin.DoLogin(profile: TProfile): Boolean;
Attempts to login into profile.
If we login, the Lobby screen is handled for you.
Returns true if we succeed.
Example:
WriteLn Login.DoLogin(profile);
Login variable¶
Global TRSLogin variable.